Frigate Deployment
Support and documentation for applications within the Stable catalog is handled by the TrueNAS community. The TrueNAS Applications Portal hosts but does not validate or maintain any linked resources associated with this app.
We welcome community contributions to keep this documentation current! Click Edit Page in the top right corner to propose changes to this article.
Frigate is an open-source Network Video Recorder (NVR) built around real-time AI object detection for IP cameras. It runs entirely locally on your hardware, ensuring your camera feeds never leave your home. This provides privacy-focused home surveillance with advanced AI features like person, vehicle, and animal detection.
Frigate uses OpenCV and TensorFlow to perform real-time object detection locally for IP cameras. By offloading object detection to a supported AI accelerator, even modest hardware can run advanced analysis to determine if motion is actually a person, car, or other object of interest.
TrueNAS Frigate app provides a complete local NVR solution designed for privacy-conscious users who want advanced AI-powered video surveillance without relying on cloud services.
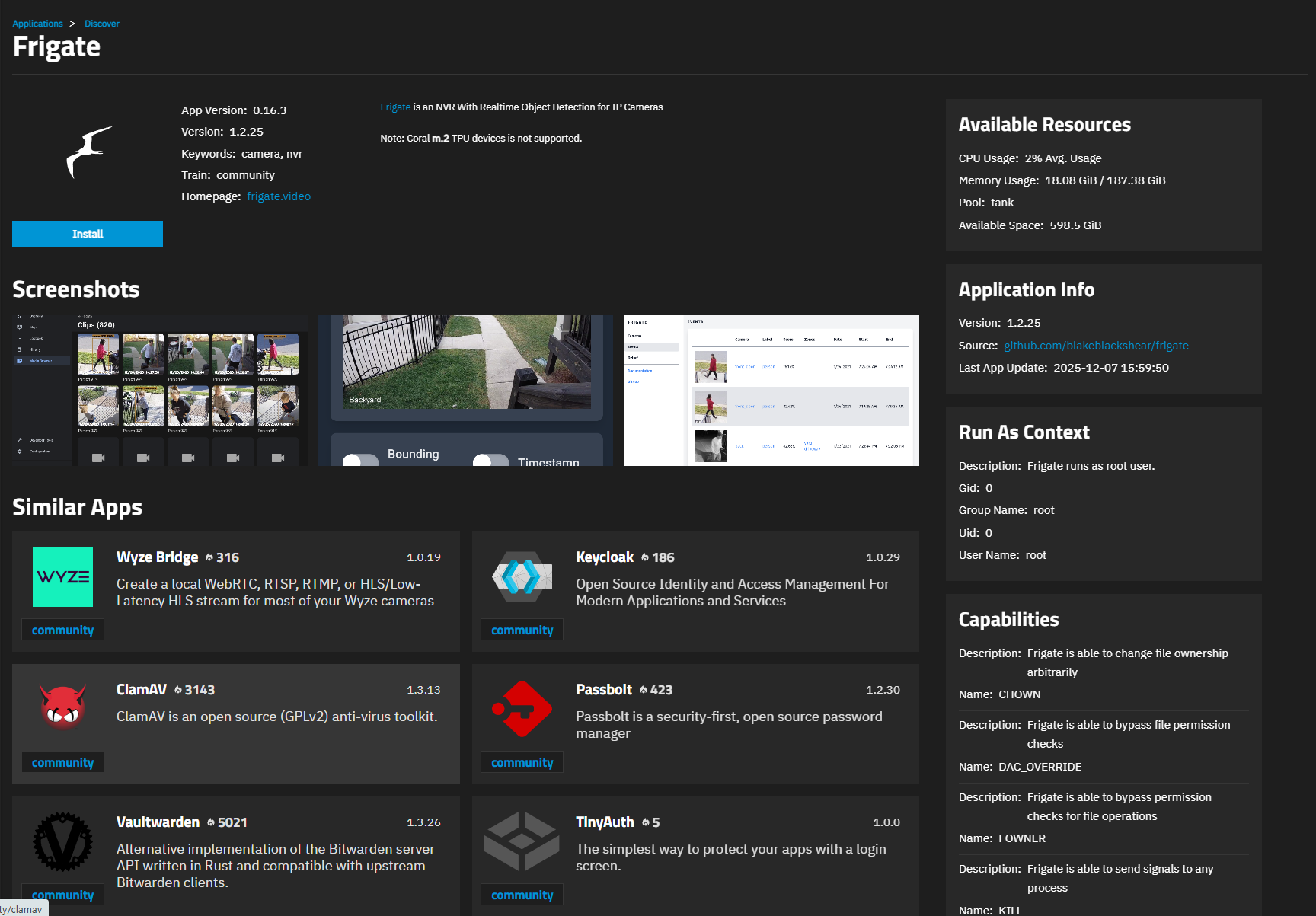
Refer to the Frigate app information screen for details on the version and release.
This procedure provides setup instructions for the TrueNAS Frigate app and how to configure it to support AI-powered object detection for your IP camera surveillance system.
TrueNAS offers one deployment option for setting up Frigate, a Linux-based TrueNAS application available in TrueNAS releases 24.10 and later.
Before you install the Frigate app:
Set a pool for applications to use if not already assigned.
You can use either an existing storage pool or create a new one. TrueNAS creates the ix-apps (hidden) dataset in the pool set as the application pool. This dataset is internally managed, so you cannot use this as the parent when you create required application datasets.
After setting the pool, the Installed Applications screen displays Apps Service Running on the top screen banner.
Locate the run-as user for the app.
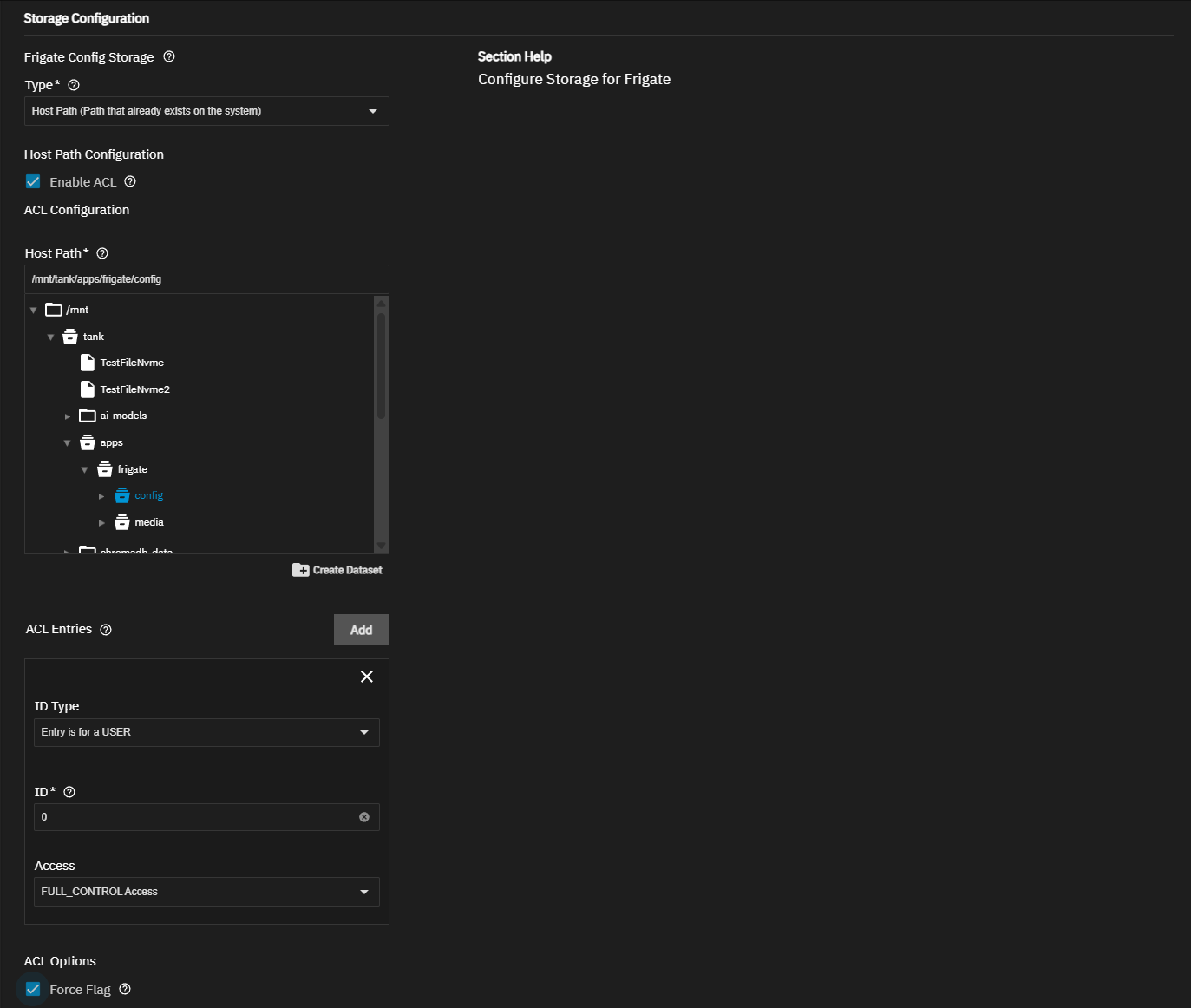
Take note of the run-as user for the app, shown on the app information screen in the Run As Context widget and in the Application Metadata widget on the Installed applications screen after the app fully deploys. The run-as user(s) get added to the ACL permissions for each dataset used as a host path storage volume.
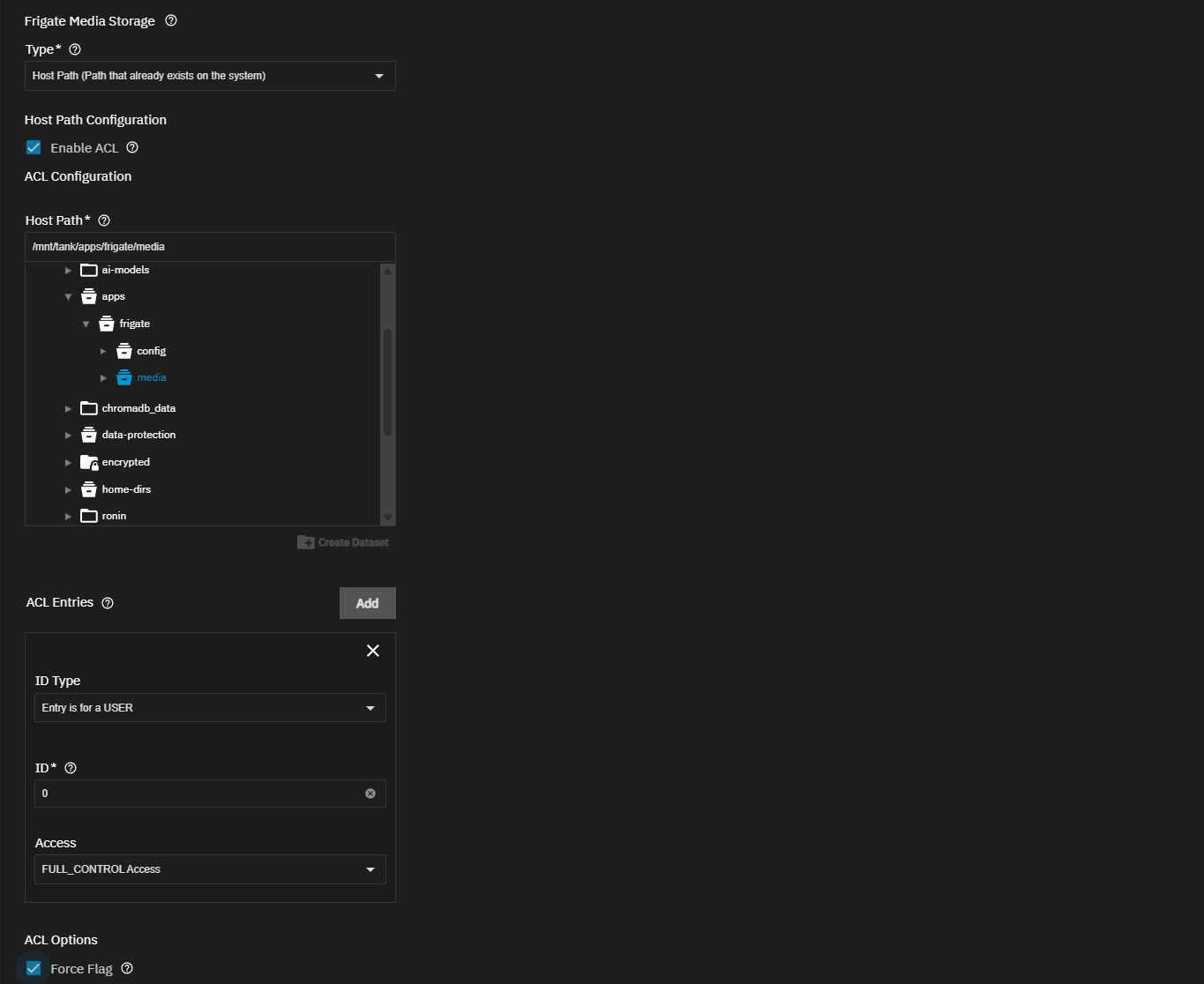
(Optional) Create datasets for the storage volumes for the app.
Do not create encrypted datasets for apps if they are not required! Using an encrypted dataset can result in undesired behaviors after upgrading TrueNAS when pools and datasets are locked. When datasets for the containers are locked, the container does not mount, and the apps do not start. To resolve issues, unlock the dataset(s) by entering the passphrase/key to allow datasets to mount and apps to start.You can create the required datasets before or after launching the installation wizard. The install wizard includes the Create Dataset option for host path storage volumes. This allows you to create the parent dataset if you want to organize the required datasets under a parent, or you can create all datasets before you begin installing the app.
To create datasets before using the Install Frigate wizard, go to Datasets and select the pool or parent dataset where you want to place the dataset(s) for the app. For example, /tank/apps/appName.
These datasets store different types of data:
- config - Contains the Frigate configuration YAML file and other app settings
- media - Stores recorded video clips and snapshots
- cache - (Optional) Stores processing and thumbnail generation, or use the tmpfs option to create a directory for temporary storage in RAM
For more information on storage configuration options, refer to the storage configuration options in the Understanding App Installation Wizard Settings section.